Thermal imaging and night vision technology are two powerful tools for enhancing visibility in low-light or complete darkness, each with unique advantages and applications. Whether you're involved in outdoor activities, security, law enforcement, or hunting, knowing the differences between these technologies can help you make an informed choice. Here, we'll break down the key distinctions between thermal imaging and night vision, covering their functions, advantages, and the best scenarios for each.
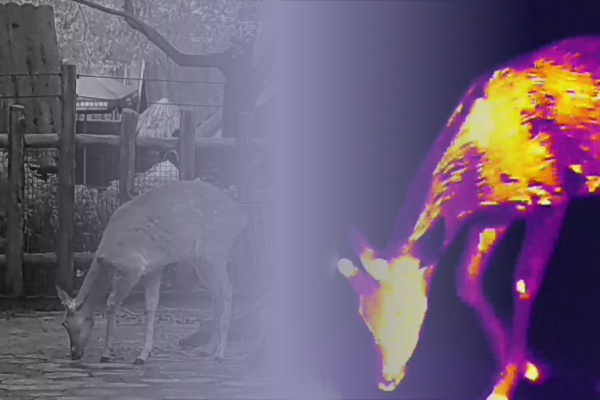

1. How Thermal Imaging Works
Thermal imaging technology detects heat emitted by objects, transforming that heat into visible images. It utilizes infrared sensors that capture the infrared radiation naturally produced by all objects, with hotter objects emitting more infrared light. This allows thermal imaging to capture images based on temperature differences, making it particularly effective in spotting warm objects like humans or animals against cooler backgrounds.
Advantages of Thermal Imaging:
- Works in Complete Darkness: Since thermal imaging detects heat, it functions effectively without any visible light.
- Sees Through Obscurants: It can penetrate smoke, fog, and light foliage, which is valuable in various challenging environments.
- Wide Temperature Detection Range: Thermal cameras can detect subtle temperature differences, making them ideal for surveillance, wildlife observation, and search and rescue.
2. How Night Vision Works
Night vision, on the other hand, amplifies ambient light (such as moonlight or starlight) to create a visible image. Night vision devices rely on image intensification technology, where photons from available light are converted into electrons, intensified, and projected onto a phosphor screen to produce an image visible to the human eye. However, in complete darkness, night vision requires infrared illumination for effective visibility.
Advantages of Night Vision:
- Enhanced Image Detail: Night vision offers sharper details and contrasts, particularly in environments with some ambient light.
- Realistic Color Tones: Newer night vision models can produce colorized images, helping with clearer recognition of surroundings.
- Cost-Effective: Night vision devices are generally more affordable than thermal imaging equipment, making them accessible for recreational users.
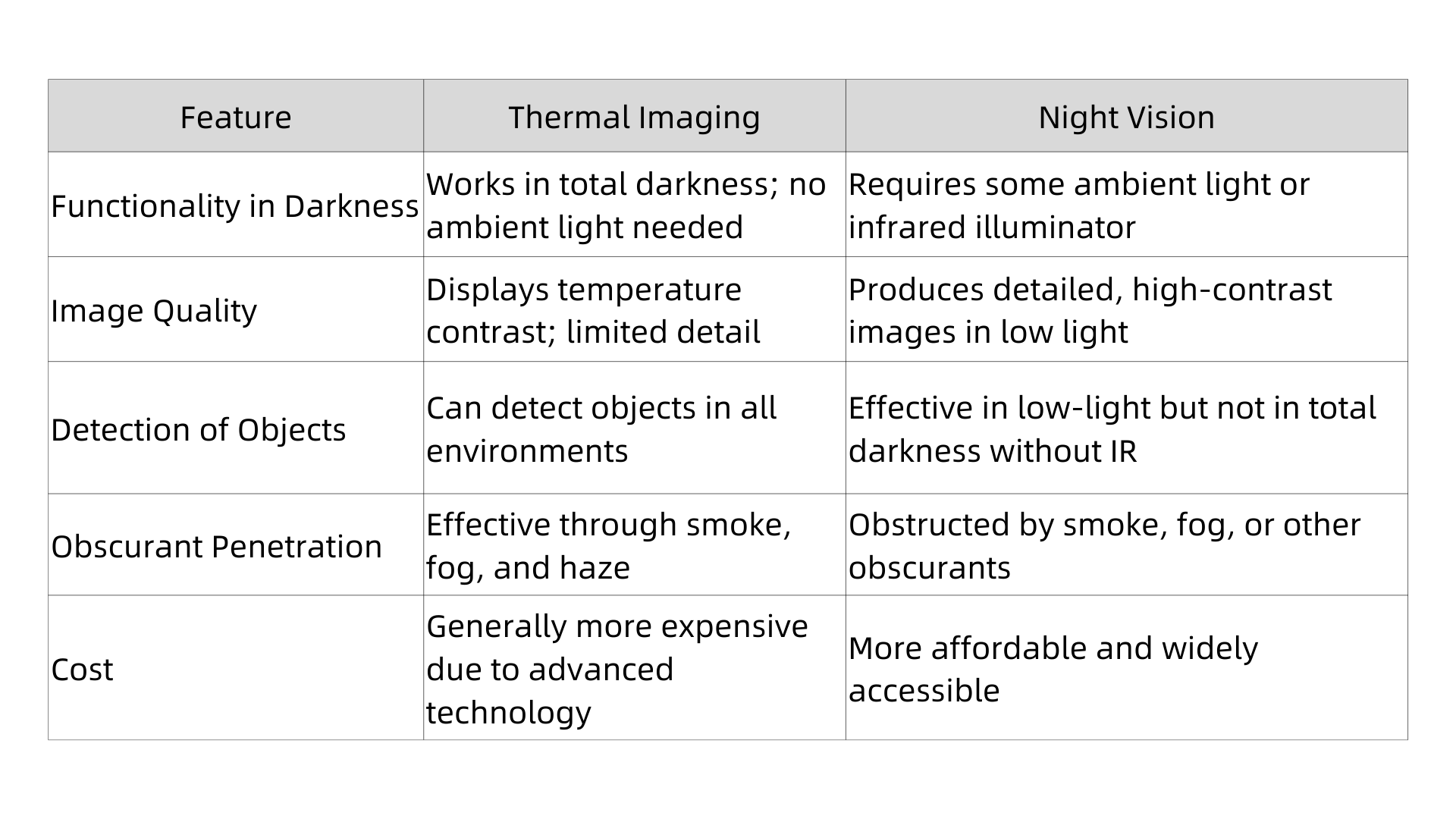
3. Key Differences Between Thermal Imaging and Night Vision
Understanding the distinctions between thermal imaging and night vision can help you determine which is better suited for your needs:
4. When to Use Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging is ideal for situations where detecting heat signatures is more important than recognizing clear details. It’s particularly beneficial in the following scenarios:
- Wildlife Observation: Spot animals without disturbing them, even at night.
- Search and Rescue: Locate missing persons or animals in difficult terrain, where heat signatures are easier to detect.
- Surveillance and Security: Monitor premises in complete darkness or through environmental obscurants like fog or smoke.
- Building Inspections: Detect heat leaks, moisture, and structural issues in buildings, thanks to temperature-based imaging.
5. When to Use Night Vision
Night vision is ideal when ambient light is present and when recognizing finer details is essential. It's suitable for:
- Law Enforcement: Situational awareness and target recognition are often clearer with night vision.
- Hunting: In low-light conditions, night vision allows for detailed visuals that can aid in tracking and identifying targets. However, when your light condition is limited, night vision may lose its function.
- Navigation: Night vision provides good visibility in low-light settings, allowing users to distinguish terrain and obstacles.
- Recreational Activities: For activities like camping or wildlife watching, night vision is more affordable and sufficient in lighted low-light settings, while infrared thermal imaging is excel in complete darkness.
6. Comparing Costs
Thermal imaging technology is generally more advanced and therefore more expensive than night vision. The price range varies, with high-quality thermal cameras costing significantly more than equivalent night vision devices. While night vision is more budget-friendly for casual users, thermal imaging’s higher price tag may be justified by its superior performance in difficult environments.
7. Making the Right Choice
To choose between thermal imaging and night vision, consider these questions:
- Do you need to see in complete darkness? Thermal imaging is preferable if there's no ambient light.
- Is recognizing heat signatures important? For detecting warm objects, thermal imaging excels.
- Are you on a budget? Night vision is typically more affordable.
- Do you need to see through smoke or fog? Thermal imaging is better suited to these conditions.
- Is detail recognition important? Night vision provides clearer details if ambient light is present.
Thermal imaging and night vision both enhance visibility in low-light environments but differ significantly in function, advantages, and costs. Thermal imaging is ideal for situations where detecting heat signatures is essential, while night vision provides better detail and is more cost-effective in ambient low-light settings. By assessing your specific needs and the environment in which you'll be using the device, you can choose the technology best suited to ensure visibility, safety, and effectiveness in any situation.
Optimize your experience by selecting the right technology for your environment!












