In the realm of infrared thermography, blackbody is a term frequently encountered when discussing the accuracy and calibration of thermal cameras. But what exactly does the term "blackbody" mean, and why is it so critical in the field of infrared thermal imaging?
A blackbody is an idealized object that has the ability to absorb all incident electromagnetic radiation, irrespective of frequency or angle. Essentially, a blackbody absorbs 100% of the radiation that falls on it, and in return, it also emits radiation across a spectrum that is dependent on its temperature. This radiation is what thermal cameras detect and measure.
When it comes to infrared thermography, blackbody calibration plays a pivotal role. By using a blackbody as a reference, thermal cameras can be accurately calibrated to ensure the correct temperature readings in a wide range of environments and applications.
A blackbody can be considered the perfect reference object for comparing any other radiation source. Its properties make it an essential tool for calibration of infrared cameras. The concept of a blackbody in thermal imaging is rooted in Planck's Law of Radiation, which describes the emission of radiation by an ideal blackbody in equilibrium. The idea of emissivity is defined using the blackbody:
Emissivity is the ratio of a radiation source’s emission to the emission of a blackbody at the same temperature.
This makes the blackbody the standard for checking how well an object or material radiates.
Using spectral emissivity, radiative sources are put into three groups:
Blackbody:
- It is a perfect emitter. Its emissivity is 1 at all wavelengths and temperatures.
- It takes in all energy and gives out the most radiation.
Graybody:
- It is a practical emitter. Its emissivity is less than 1 but stays the same at all wavelengths.
- It gives off radiation evenly, based on a blackbody at the same temperature.
Selective Emitter:
- Its emissivity changes depending on the wavelength.
- It is common in real materials. Radiative properties depend on what it is made of and its surface.
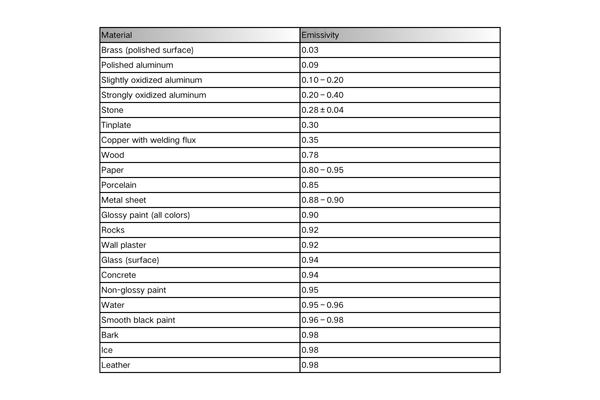
Common Emissivity Values for Materials
Below is a table of common materials and their emissivity values: